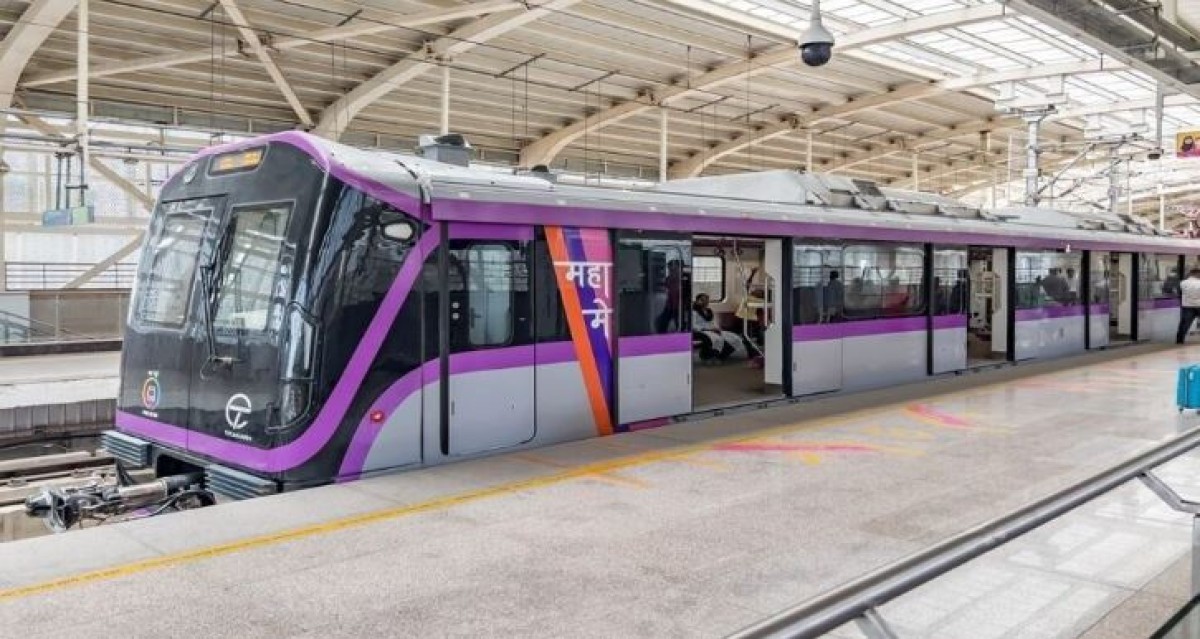
Maharashtra Metro Rail Corporation Ltd plans to add station at Balaji Nagar on Swargate-Katraj Underground
Maharashtra Metro Rail Corporation Ltd has requested approval from the Pune Municipal Corporation on the request of elected representatives to conduct an additional Metro station at Balaji Nagar along with Swargate-Katraj underground route. The proposal which was presented to the civic standing committee Municipal Commissioner Rajendra Bhosale informed that Maha-Metro has sought approval at Balaji Nagar. Nevertheless, the PMC has been counseled to grant approval with the condition that the project sustains no additional costs to the civic body. Maha-Metro, a joint venture between the central and state governments has also insisted the PMC give in primary approval for the additional stations on the Swargate-Katraj Underground Extension Line. This extension will be sanctioned by the PMC in 2021 which spans 5.463 km and includes three underground stations with the total project cost of Rs 2,954.53 crore.















Leave a comment